- Mac Redis Server
- Redis Connection Refused Mac High Sierra
- Redis Connection Refused Mac Os
- Redis Connection Refused Mac Catalina
- Redis Connection Refused
- Redis Connection Refused Mac Download
Redis is a very popular data store used across all kinds of web apps it’s supported natively by Mac and Linux operating systems. Heck, you can even use Docker to run Redis. The purpose of this guide is to setup Redis so we can use in our Python applications including Django, Flask. There is redis service running on centos 7.6 it looks fine there,(192.168.0.24:6379) I try to connect this client from another machine in same network(192.168.0.22) There is incoming request from. These didn't generate any errors; however, it appears that Redis does not start. If I run redis-cli ping, I get back Could not connect to Redis at 127.0.0.1:6379: Connection refused. I can manually run redis-server in another terminal window, but I'd like to have Redis auto-start on login. Tony@kali:$ redis-cli Could not connect to Redis at 127.0.0.1:6379: Connection refused Could not connect to Redis at 127.0.0.1:6379: Connection refused not connected redis share improve this question follow.
So you dressed up your terminal with your favorite bash profile, tuned up your monitor lighting to an ambient level and your favorite chillstep music is playing in the background, in other words, you’re ready for Redis and Chill. Welcome to our tutorial series on how to master the art of Redis!
What is Redis?
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes with radius queries. Redis has built-in replication, Lua scripting, LRU eviction, transactions and different levels of on-disk persistence, and provides high availability via Redis Sentinel and automatic partitioning with Redis Cluster.
Created by Salvatore Sanfilippo aka antirez, Redis is one of the most popular piece of software on the web! I’m very excited to give you a tutorial today and I hope to demonstrate you the power behind this amazing database.
Installation
You don’t need to have Redis installed in order to start try out commands, but we’re all about being practical, so I’m going to show you how to install Redis in three different ways:
- Standard installation
- Digital Ocean pre-build droplet
- Docker Container
Standard Installation
Assuming you’re on a *nix based OS (sorry Windows users):
Head over to http://redis.io/download, download the current stable version (3.2.3 at the time of writing):
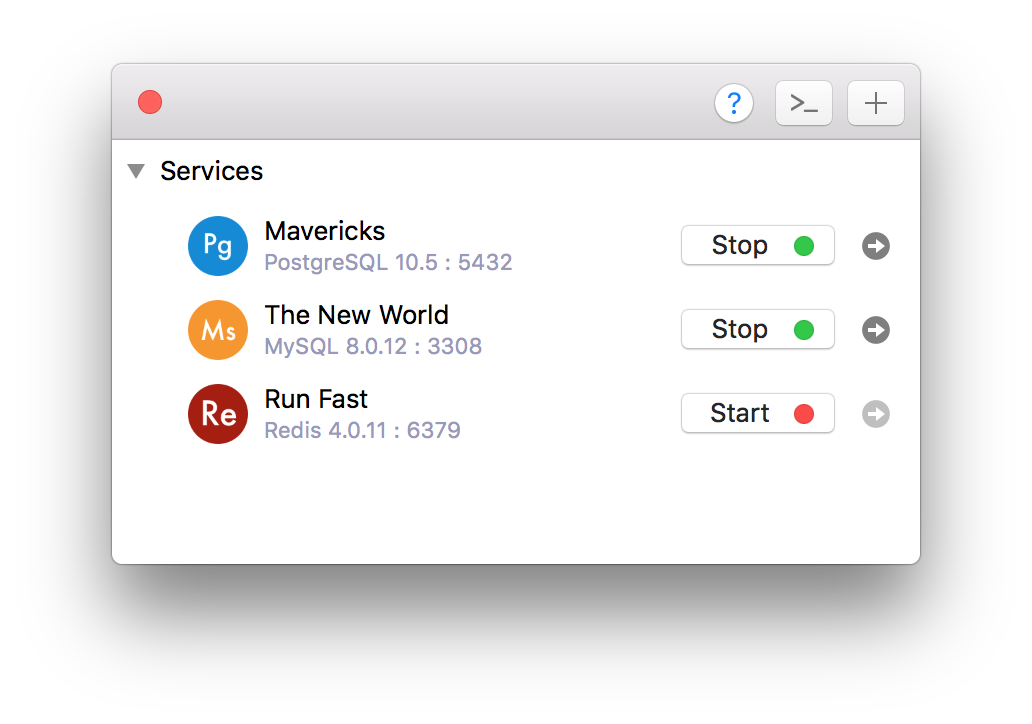
verify redis is working by turning on Redis Server in the background
then open another terminal tab and start a Redis Client by:
When you see the terminal prompt changed into
type in INFO
and you should see something like this:
That’s it! Fast and simple. Now you don’t want to run Redis server in a new tab everytime you need to develop your app, so we should make Redis Server to run automatically in the background.
Follow this tutorial if you’re running on Mac.
Digital Ocean Pre-built Droplet
The fastest, easiest way for us to set up a fresh server with Redis pre-installed, is via a Digital Ocean droplet. Digital Ocean is an amazing cloud hosting company similar to AWS, Google App Engine or Microsoft Azure where you can start your own private servers. If you would like an intro tutorial on Digital Ocean, I recommend you to read my tutorial on How to create a blog in 5 minutes with Digital Ocean
Ok, head over to Digital Ocean, assuming you’re signed in, we’ll need to create a droplet (a droplet is Digital Ocean’s term for a server), select Redis 3.2.1 on 14.04 under One Click Apps:
Select your droplet size and location and name it something you can easily reference it by, then click Create to launch your server. Within 60 seconds, you will receive an email with password to your server! That’s it, that server now has Redis pre-installed.
To test it out, SSH into the server
enter the password that was sent to you to your email and you should be able to log in:
follow the instruction above from the Standard Installation section and you should see a similar screen that displays your Redis server information.
Your remote Redis server is now set up! If you wish to connect to it, you would do this on your local server:
Hmm, why is this not working? That is because by default, Digital Ocean turned off connections to the server from outside. This is a good security practice because only IPs from a whitelist can connect to the server.
For the sake of this example, let’s let anyone from anywhere connect to the server.
On your droplet, type:
This will open up your Redis Config file using Vim, we need to look for the line:
and comment it out
You also need to turn off Protective Mode by changing this line from:
to
Save (:wq) and restart the Redis Server by:
Now on your local computer, connect to the Redis droplet by
where 104.131.18.33 is your server IP, and you should be able to connect and run the INFO command!
Of course the above was just to demonstrate how you would connect from a remote location, in practice, you should always limit connection with an IP whitelist and set a password to your Redis server. Digital Ocean’s droplet comes with a lot of best practices built in, so it’s definitely my preferred method of installation.
Docker
Docker is the one of the hottest Containerization technology around the block. With Docker, you can isolate Redis on a “container” on your computer to reach true isolation while maximizing your server utilization, This part of the tutorial is useful if you are thinking about adding Redis to your existing stack. If you need an intro to Docker, you can read about my tutorial here: Using Docker to deploy Apache, Nginx, WordPress and Nodejs containers with Digital Ocean and Creating a LEMP stack with Docker Compose
To start, we need to create a directory on either your local machine or your server:
open up your favorite editor and edit the docker-compose.yml file, in my case I use Visual Studio Code:
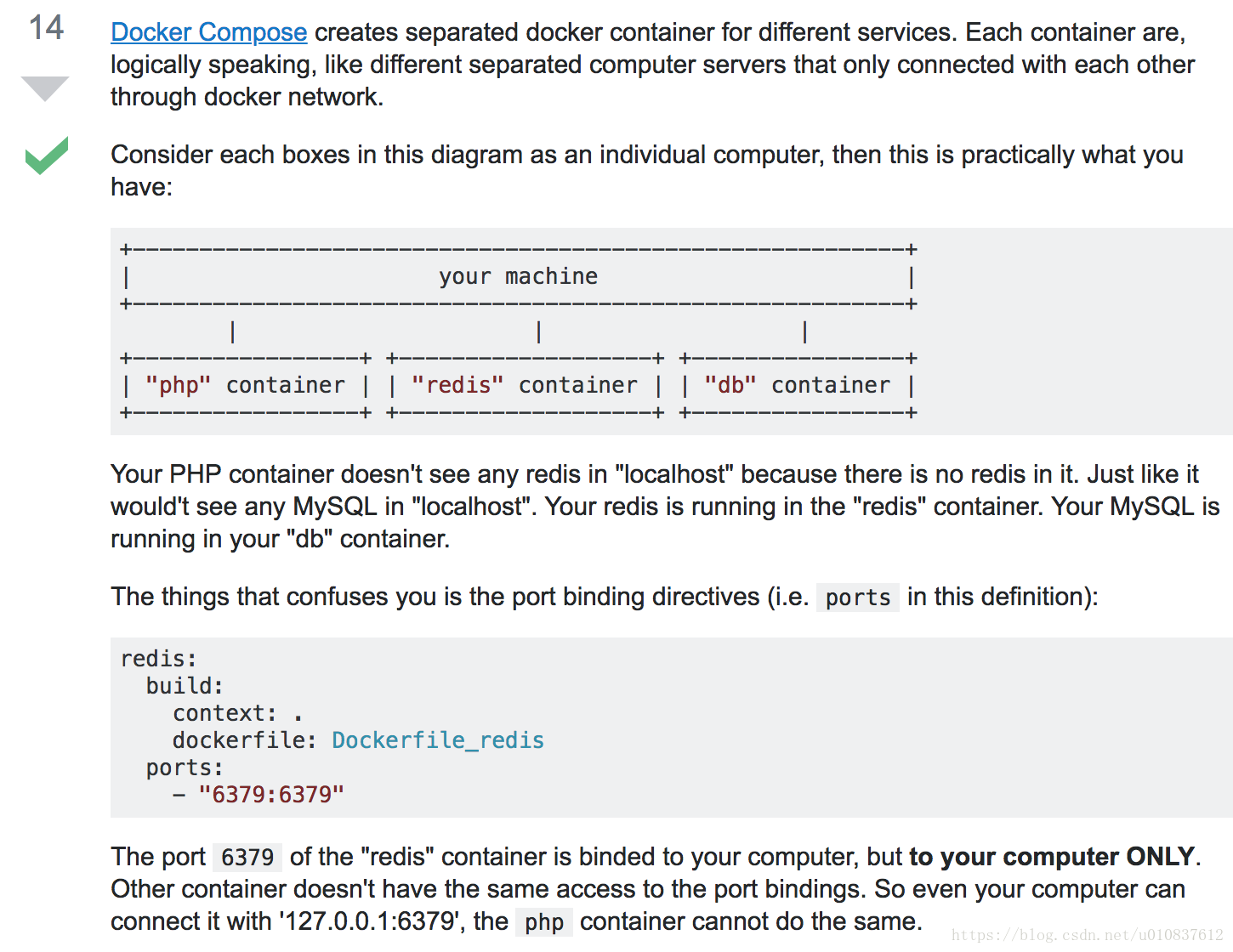
We’re going to install Redis and a very helpful companion app call Redis Commander.
Start a docker terminal session and type:
Mac Redis Server
and you should see your containers being created:
believe it or not, we’re done! Now we should be able to connect to the containerized Redis server from inside Docker. Let’s find the IP address of the container instance:
this will return the IP of our docker virtual machine. In my case it returned 192.168.99.101 , we also know the port of our Redis server because we defined it in our docker-compose file, the port to the redis server is 9000. Now that we have the information we need to connect to our Redis instance, let’s start a connection.
With our local Redis client installed, we can connect to our container via the following command:
Amazing isn’t it? Let’s set a key in Redis so we can demonstrate the power of Redis Commander:
Redis Commander was set up on port 9001, so we need to head over to http://192.168.99.101:9001/ in order to access the web UI:
The UI is really straight forward, now you can VISUALLY see all your keys and perform operations on them!
Head over to Redis Commander website for more info on what it’s capable of.
Of course the above Docker workflow can be performed within your Digital Ocean droplet as well (Digital Ocean also provide droplets pre-built with Docker).
That is it for our intro lesson! We went over three ways to set up Redis today, and we set up Redis Commander to help us see our data inside Redis better. Next time we’ll talk about how we can use what we setup today to power our applications. I’ll see you there!


If you enjoyed this tutorial, make sure to subscribe to our Youtube Channel and follow us on Twitter @pentacodevids for latest updates!
RedisInsight
Update: In April 2019, we acquired RDBTools from HashedIn and created its successor RedisInsight, a browser-based management interface for your Redis deployment. Learn more and download it here.
It all comes down to preferences. While there are Redis users who are familiar with the Redis command line interface (CLI) and rely on it to inspect, visualize and perform manual updates, there are those who prefer to using a Graphical User Interface (GUI) to achieve that. There are several Redis GUIs available, for different platforms, and in this article I’ll try to review a few of them.
Important: Before using any of these tools in production, keep in mind that some GUIs rely on the (“evil”) KEYS command. Should you have a large database, your Redis server might freeze and cause issues in your production applications.
Redsmin: My Go-To-Tool for the Cloud (and Below)
I’m starting off with Redsmin – my personal favorite. It mixes perfectly my on-the-go needs with a sane and objective way to work with my databases. It is a different kind of offering as it is a web based service that offers not only a GUI for inspecting your Redis data, but also monitoring and runtime server reconfiguration. Redsmin provides several plans, including a free one that can be used to evaluate a small dataset (up to 100,000 keys). Since redsmin is a hosted service, connection to your Redis server can be done directly over the internet, optionally SSL authenticated and encrypted, or by using a proxy service that you run on your servers that exposes your Redis instances to Redsmin in a secure way.
Redsmin has plenty of extra features, such as slowlog inspection, a list of currently connected clients that allows you to disconnect them, a multi keys editor for batch operations and great search features. With plans starting as low as 5,99€/mo, you can lift all limitations and connect to multiple Redis instances.
Pros: the most extensive features set, ease of use, no install
Cons: requires an internet connect, anything else contact Redsmin’s awesome support.
Redis Commander: A Free Node.js Powerful Choice
Redis Commander is a Node.js web application that can be used to view, edit and manage your Redis databases from the comfort of your browser. It allows you to directly manipulate all of Redis’ data types. It’s freely available (although it doesn’t specify under which license) and can be easily installed via npm, provided you have a working node.js installation.
Like most Redis GUIs, Redis Commander allows you to connect to multiple database and Redis server instances simultaneously. Besides having an editor, Redis Commander also includes a terminal with auto completion (for both commands and keys), documentation and import/export functionality.
Redis Commander does require direct access to your Redis servers, but you can get around that by running it directly in your Redis servers so you can access it remotely without having to expose your Redis server over the internet.
Pros: it’s free, powerful, in your browser and runs wherever Node.js is.
Redis Connection Refused Mac High Sierra
Cons: requires direct connectivity, only runs where Node.js is.
Redis Desktop Manager: Cross-Platform, Pure Desktop GUI
Redis Desktop Manager is a cross-platform desktop Redis client, available for Windows, MacOSX and Linux desktops. It’s freely available under the MITLGPL license.
Redis Connection Refused Mac Os
Like most other Redis GUIs, it allows you to connect simultaneously to multiple Redis databases or instances, inspect and modify your data and use an interactive terminal. You can also search for keys across multiple databases and view a system console which logs all Redis commands.
However. One unique feature of Redis Desktop Manager is that it allows you to establish connections via SSH tunnels, enabling secure connections to remote servers.
Pros: free, dead simple installation, runs on the desktop, SSH tunneling a breeze
Cons: if you’re comfortable using a desktop GUI, there are none. Update: there seems to be a minor issue with OpenGL under a VM that’s fixable as instructed here (hat tip: Adam Christie).
Induction: You Can Guess By the Name That It’s for Mac OS X
https://inductionapp.com/
UPDATE: the project has been discontinued.
Induction is a Mac OS X database client. It’s not Redis specific as it also supports PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite and MongoDB, and therefore isn’t the the most complete Redis GUI. Nevertheless, it allows to inspect and query your Redis database. Similarly to other Redis clients, it requires a direct connection to your server.
Redis Connection Refused Mac Catalina
The alpha version is free available under an open source license.
Pros: An holistic view on polyglot persistency
Cons: limited Redis-specific functionality, MacOS-specific
redis-browser: The Runner Up
Redis Connection Refused
This web-based explorer view of your Redis database is delivered as a Ruby gem. It is the youngest of the tools in this review and probably the simplest. Simplicity, however, is sometime a virtue, especially when you need a no-frills, dead-simple GUI. Give it a shot and encourage @Monterail to keep up the good work!
Conclusion
Redis Connection Refused Mac Download
There are several other Redis GUI alternatives that are available, both for the desktop and ones that are web-based, with similar characteristics to the ones shown here. The ones highlighted here are the most popular and actively developed, but YMMV. They were picked as examples to allow developers that are less CLI-savvy to gain insight into their Redis databases and quickly perform some updates. If you have other favorites tellme – I’m highly available 🙂